10 Science Based Benefits Of A High Protein Diet
Wondering what to eat to keep you energized, healthy, and maybe even shed a few pounds. The answer might be simpler than you think. Welcome to the world of high-protein diets!
Whether you’re looking to build muscle, lose weight, or just feel your best, a high-protein diet can be your secret weapon.
In this article, we’ll dive into why protein is so crucial and explore ten science-backed benefits that will make you want to add more of it to your plate. So, let’s get started!
What Is A High Protein Diet?

A high-protein diet focuses on increasing your intake of protein-rich foods while moderating your consumption of carbohydrates and fats. Protein is a micronutrient essential for building muscle, repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and supporting overall health.
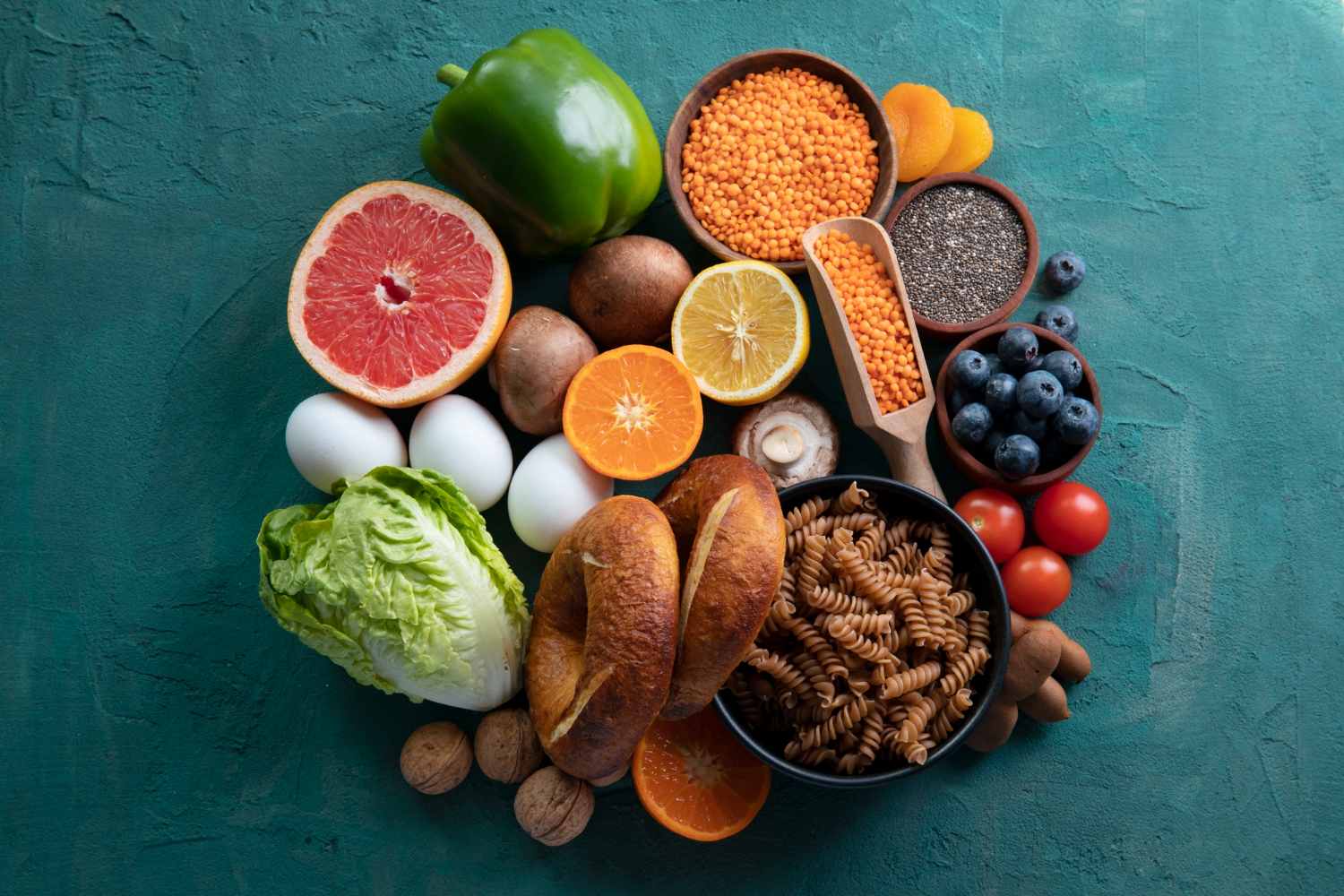
Examples of High-Protein Foods:
Meat: Lean cuts of chicken, beef, pork, and lamb are excellent sources of protein. Opt for grass-fed or organic meats when possible for higher quality.
Fish and Seafood: Salmon, tuna, shrimp, and mackerel are not only rich in protein but also provide healthy omega-3 fatty acids that are beneficial for heart health.
Dairy Products: Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, and milk are dairy options packed with protein and essential nutrients like calcium and vitamin D.
Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, black beans, and soybeans are plant-based protein sources that also provide fiber, which is great for digestion.
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, peanuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are high in protein and healthy fats. They make excellent snacks or additions to meals.
Eggs: A complete protein source, eggs are versatile and nutrient-dense. Both the whites and yolks provide essential nutrients.
Protein Supplements: Whey, casein, and plant-based protein powders can be convenient options for those needing to increase their protein intake quickly, especially after workouts.
10 Science Based Benefits of a High-Protein Diet

1. Reduces Appetite and Hunger Levels:
High-protein diets can help you feel fuller for longer. Protein reduces levels of the hunger hormone ghrelin while boosting peptide YY, a hormone that makes you feel full. This means you’re less likely to reach for unhealthy snacks throughout the day.
2. Increases Muscle Mass and Strength
Protein is essential for muscle growth and repair. Consuming adequate protein, combined with strength training, can help you build and maintain muscle mass. This is especially important as we age since muscle mass naturally declines over time.
3. Increases Your Metabolism
Eating protein can boost your metabolism because it has a higher thermic effect compared to fats and carbs. This means your body uses more energy to digest protein, which can help you burn more calories throughout the day.
4. Aids in Weight Loss and Weight Management

According to a journal of Cambridge University, High-protein diets are effective for weight loss because they help control appetite and increase feelings of fullness. Studies have shown that people who increase their protein intake can lose weight and maintain their weight loss more effectively than those on lower-protein diets.
5. Reduces the Risk of Heart Attacks, and Chronic Kidney Disease
Protein can improve your heart health by lowering blood pressure, reducing LDL cholesterol, and decreasing triglycerides. These benefits collectively reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and chronic kidney disease.
6. Helps Speed Up the Recovery Process After an Injury
Protein is crucial for the repair and regeneration of tissues. If you’ve suffered an injury, increasing your protein intake can help speed up your recovery process by providing your body with the necessary building blocks for repair.
7. Controls Cholesterol Levels
A high-protein diet can help manage cholesterol levels. Protein-rich foods like fish, nuts, and legumes contain healthy fats that can improve your cholesterol profile by increasing HDL (good cholesterol) and lowering LDL (bad cholesterol).
8. Good for Your Bone Health
Contrary to popular belief, protein can benefit bone health. High-protein diets have been shown to preserve bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures, particularly in older adults.
9. Maintains Fitness as You Age

As you age, maintaining muscle mass and strength becomes more challenging. A high-protein diet can help you preserve muscle, keep fit, and improve your overall physical function, reducing the risk of falls and injuries.
10. Improves Your Sleep

Protein can improve sleep quality by increasing the production of serotonin, a hormone that regulates sleep. Eating a protein-rich snack before bed, such as a small piece of chicken or a serving of Greek yogurt, can help you fall asleep faster and enjoy a more restful night.
How Much Protein Should You Eat Daily?

The amount of protein you need depends on several factors, including age, sex, physical activity level, and overall health. According to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for protein is 46 grams per day for women and 56 grams per day for men.
However, many experts suggest higher intake levels for optimal health and fitness benefits.
Here’s a chart outlining the recommended protein intake for different ages and activity levels:
| Age Group | Recommended Daily Protein Intake |
| Children (4-8) | 19 grams |
| Children (9-13) | 34 grams |
| Teens (14-18) | 46-52 grams |
| Adults (19-50) | 46-56 grams |
| Older Adults (50+) | 46-56 grams |
| Athletes | 1.2 to 2.0 grams per kg of body weight |
For example, a sedentary adult might need around 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, while an athlete might require up to 2.0 grams per kilogram. It’s important to adjust your protein intake based on your individual needs and lifestyle.
How to Incorporate a High-Protein Diet in Your Daily Life?

Start Your Day with Protein: Include protein in your breakfast to kickstart your metabolism. Options like eggs, Greek yogurt, or a protein smoothie can be great choices.
Balance Your Meals: Ensure each meal contains a good portion of protein. Combine it with vegetables and whole grains for a well-rounded plate.
Snack Wisely: Choose high-protein snacks like nuts, seeds, or protein bars to keep your energy levels steady throughout the day.
Plan Ahead: Prepare high-protein meals and snacks in advance to avoid reaching for unhealthy options when you’re hungry.
Diversify Your Sources: Mix and match animal and plant-based proteins to ensure you get a variety of nutrients and keep your meals interesting.
Final Words:
Incorporating more protein into your diet can bring a multitude of health benefits, from reducing hunger to improving muscle mass and even aiding in weight loss. Remember to choose high-quality protein sources and balance them with other essential nutrients for a well-rounded diet.
So, go ahead and make protein a priority in your meals—you’ll likely see and feel the benefits in no time!